MDIX ProductsMDIX’s Interoperability Solutions employ a model driven architecture. At the core of this approach is transforming one format to another, be they an industry standards, those of a healthcare vendor and HIEs, or you own internal formats. In addition to managing change, this model driven approach provides the following benefits: Reusable and shareable
Any transformation model works with any other transformation model
Open SourceMDIX uses open source MDMI software and content providing services for all aspects of MDMI processing including:
More information is available at GitHub |
|

MDIX Transformation Model WorkbenchMDIX Transformation Model Workbench is used to create and maintain any transformation model for any format. There are two components to the Workbench, the MDMI Map Editor and the MDIX Semantic Element Exchange Registry (SEER). MDMI Map EditorThe Editor is the end-user application for creating and modifying transformation models, which we call maps, and offers these productivity capabilities. Productivity for Model Developers.
Productivity for other Team Members
|

|
MDIX Semantic Element Exchange Repository (SEER)The MDIX SEER is a cloud-based service that is the keystone of MDIX Transformation Model interoperability. Through the SEER, any MDIX map can interact with any other MDIX map developed by you or anyone else. The MDIX SEER contains the business concepts exchanged in healthcare information. It embodies every clinical and administrative healthcare concept needed in industry standard exchange formats as well as other concepts. New content is easily added when new business concepts have been identified. |

|

MDIX Purpose Built Runtime Products
MDIX offers three products addressing the major functions of message exchange, each optimized for its specific purpose. We understand that our interoperability products are a component of your solution, so we package them as software services employing industry standard interfaces. Our objective is to make integration into your systems a configuration exercise, not a software development project.
|
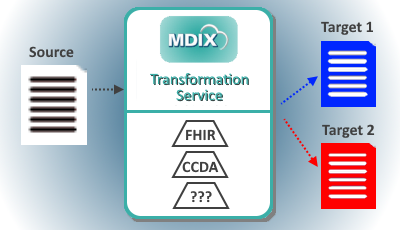
MDIX Transformation ServiceThe most basic service is the transformation of a source file into a target file. This capability is central to many use cases. Examples include
The MDIX Transformation Service provides added value components to core transformation capabilities such as
|
|
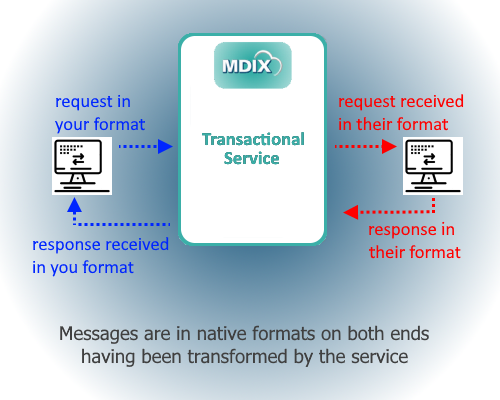
MDIX Transaction ServiceProvides additional capabilities to the MDIX Transfromation Service, this provides query capabilities for handling dialogues between a sending organization and receiving organization. The product incorporates sending of a request and transforms the request into a form the receiver can process. Then using the MDIX Transformation Service it transforms the receiver response into the sender format. Some example use cases are
|
|
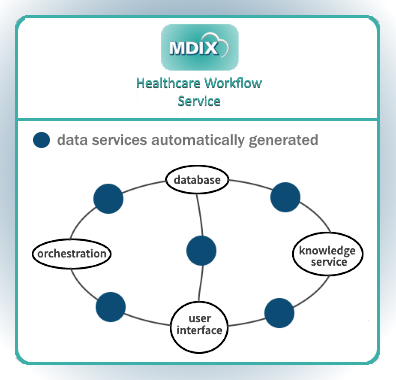
MDIX Healthcare Workflow ServiceDelivering high quality, individually patient-centered treatment, sometimes referred to as Clinical Pathways, is the goal of every healthcare provider and their partners. It is impossible to achieve this goal without IT involvement. Healthcare IT cannot achieve this unless its implementations can interoperate with and integrate with others for
Interoperability solutions are a core capability for Healthcare IT to deliver on this goal. MDIX stands alone delivering a dynamic, robust, high quality service as an interoperability solution for Clinical Pathways. As a founding member of the BPM+ Health Consortium, MDIX has demonstrated our ability to knit together, in a configurable fashion, different vendor and provider shareable solutions. Solutions that dynamically capture information based on a situation, incorporating rules of the situation then deliver information necessary to the next IT component based on the Clinical Pathway. Our ability to dynamically discover situational information combined with our model driven approach to isolating and then implementing change makes us unique. |

